Learn How Stress Affects the Immune System, Leading to Infections
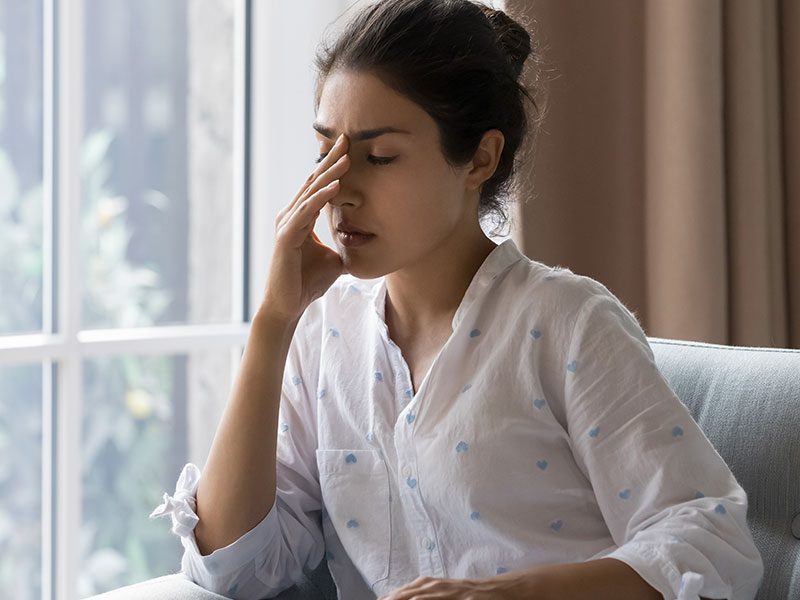
As we think about health, the obvious references we make are usually diet, exercise, or hygiene. But mental health aspects, which are often neglected, are important components of general health. One of the main links between mental and physical health is through your immune system, and that can tell you a lot. When people suffer from stress, depression, or anxiety, their bodies have the process of dealing with infections, injuries, or diseases way harder.
What Are the Main Factors That Impact Your Immune System?
Let us quickly review the key aspects affecting our immune systems before we connect mental health with infection. The immune system is the part of the body that serves as a barrier against harmful bacteria and viruses as well as other forms of intruders. The strength and efficacy of an individual’s immune system depend on several factors:
- Nutritional Value: A sufficient intake of vitamins and minerals alongside antioxidants would help in boosting immunity.
- Rest: Adequate sleep is important for regenerating the cells responsible for immunity to function best.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercises will promote immune responses.
- Water Intake: Individuals who are well-hydrated produce lymph, a vital fluid that carries white blood cells and nutrients to various tissues in the human body.
- Mental Well-Being: This one gets really interesting. To put it briefly, mental health includes issues such as stress, depression, and anxiety that negatively affect how your immune system works.
Understanding Stress’s Impact on the Immune System
Stress is inevitable. It’s true for everyone that at some point in his or her life, one will experience stress, be it because of work, relationships, or other everyday pressures. While a little stress might be motivating, chronic stress is a big threat to your health.
The impact that stress has on the immune system is that the moment you feel stressed, your body starts to pump out very high levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline. The moment that the stress is extended, that can set off a permanent state of immunosuppression. Chronic stress reduces immunological efficiency by reducing the production of white blood cells, which are important in fighting infections.
This increased stress will eventually lead to consequences even more detrimental to the immune system: poor eating, lack of exercise, and inadequate sleep. All these factors combined may put you at greater risk of infections and really slow you down in being able to recover from illness.
How Your Body Parts Signal About Stress Being Harmful
When stress becomes chronic, your body can begin signaling the damage in ways that may not at all be immediately obvious but are important to recognize. Stress initiates a variety of responses, starting with the release of cortisol and adrenaline to prepare your body for a fight or flight situation. While those hormones prove quite useful when considering short-term bursts, they can create a host of health problems when sustained over longer periods.
It may be manifested by your cardiovascular system through palpitations and rising blood pressure, thereby increasing the risk for conditions like hypertension or heart disease. Stress may further weaken your immune system so that you may become more susceptible to infections. Muscles tighten up, and chronic pains set in; usually, it goes further to include headaches or even migraines. The digestive system takes an equal hit with stress, bringing in symptoms such as indigestion, irritable bowel syndrome, or flare-ups of ulcers.
Aside from the physical manifestations, it can also impair cognitive functions and lead to a decrease in concentration and memory. These are your body’s warning signs that it is taking a toll from prolonged stress and should be heard. Stress can be dealt with through relaxation techniques or medical intervention, which can prevent these signals from becoming major health issues. But if your body is seriously hurt due to stress, internal medicine can become the field that helps you to deal with the consequences.
How Internal Medicine Deals with Stress Issues
Internal medicine has different approaches to mitigate the stress-immune consequences. Your Internist will accomplish this by restoring balance either with medications, changing certain lifestyle choices, or teaching stress management skills. For example, they may prescribe medications that will stabilize blood pressure or level mood in cases of depression and anxiety, thus minimizing the immune suppression effect from chronic stress. They also often suggest regular physical activity, sufficient sleep, and dietary changes that could favorably affect immune function and overall well-being.
Internal medicine doctors are also keen on routine checkups and vaccinations to ensure that even when your body’s defenses are compromised due to stress, the patient is still safe from infections. They enhance immune responses to infections and quicken recoveries both by addressing the physical and mental aspects of stress and your immune system.
Infection Recovery and Stress: The Delicate Balance
Your body needs all the help it can get when you’re fighting off an infection. Infection recovery and stress mix like oil and water. Recovering from sickness takes energy, rest, and a healthy immune system. If you’re stressed while you’re trying to recover, though, that process could be slowed tremendously.
It can hurt your sleep; that’s important in recovery. Again, it can result in bad eating habits; hence, it deprives the body of food necessary for recovery. Moreover, stress is usually the main determinant in sticking to recovery protocols: taking medications on time, attending follow-up appointments, among others.
Part of ensuring that patients make a smooth and fast recovery is effective nutrition and vitamin intake. Your doctor will look at the results of your health exam and provide you with guidance on how you should act to recover faster and not let infection outfight you. Remember, trying to deal with serious health conditions on your own is not the best idea; visiting a healthcare professional is the right thing to do.
Summing Up…
It’s more than just feeling good; understanding the connection between your immune system and stress is important for good health. The impact of stress on the immune system or how depression affects it only goes to underline the importance of good mental health in the prevention, but also recovery, from infections.
Knowing how internal medicine deals with the consequences of stress helps in decreasing infection risk and enables us to act to support the immune system in appropriate ways. You should remember that visiting a healthcare professional is the best thing to do, as having someone with experience look at your case is the key to managing every concern.